Study and Analysis of the Effect of Suction Parameters on the Performance of Different Air Compressors in Textile Enterprises
2024-03-11
Compressed air Suction Parameters is the second largest power source for textile enterprises after electricity, and it is clean, safe and easy to use. In most textile enterprises, the energy consumption of the air pressure system accounts for 30 percent or even more than 40 percent of the total energy consumption of the enterprise, because the production of compressed air is a high-energy process. A typical compressed air system consists of three parts: generation, delivery and use of compressed air, and the air compressor is the air source device for compressed air, which is the most important part of the whole system, and its power consumption accounts for 96% of the total power consumption of the system. When the suction temperature of the air compressor rises by 3°C, the power consumption of the air compressor will increase by about 1%. Compressed air from the atmosphere, with the passage of time its temperature and humidity will fluctuate, this fluctuation will be on the air compressor and even the whole system has an unavoidable impact.
The air compressor draws in high temperature and high humidity air for compression, which will lead to the decrease of its exhaust volume and exhaust pressure, and the increase of energy consumption. Therefore, to analyse and study the impact of suction parameters on the energy consumption of air compressors, and to take positive measures to reduce the suction temperature and humidity of air compressors has become the primary work of textile enterprises to reduce energy consumption. This paper firstly introduces the air compressors commonly used in textile enterprises and their working principles, then introduces the commonly used air compressor performance analysis methods, and finally discusses the influence of suction parameters on the performance of air compressors by using a combination of experimental tests and theoretical calculations for the PM VSD screw air compressors and centrifugal air compressors commonly used in textile enterprises.
1. Textile Enterprises Commonly Used Air Compressor and its Working Principle: Suction Parameters
There are many ways to classify the air compressor, according to the different working principles can be divided into two categories of speed type and volumetric type, in which the speed type air compressor is divided into axial, centrifugal and mixed flow type; volumetric air compressor is divided into piston type, membrane type, slide type, screw type and rotor type. At present, the air compressor commonly used in textile factories is the centrifugal air compressor in the speed type air compressor and the screw air compressor in the volumetric air compressor.
1.1 Principle of Operation of Centrifugal Air Compressors
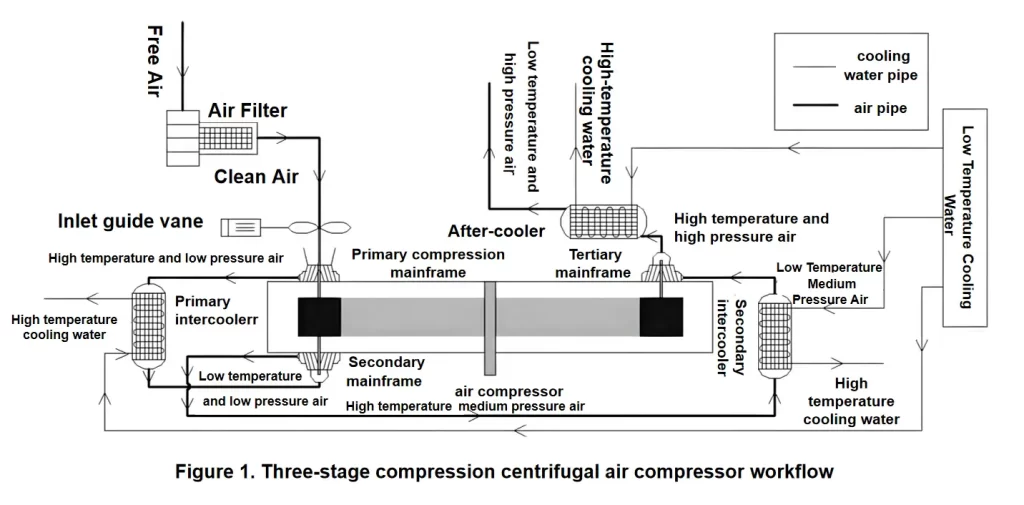
Centrifugal air compressor converts the kinetic energy of impeller into pressure and kinetic energy of air. When working, the impeller at all levels of the host rotates at high speed, so that the air is subjected to centrifugal force to generate pressure at the same time of obtaining the flow, and the air leaves the impeller through the diffuser, the expansion channel and other pressure expanding devices, which converts the kinetic energy into pressure energy, and further enhances the air pressure.
At the same time, the low-temperature cooling water cooled by the cooling tower flows into the cooler, and then flows out of the cooler after the heat exchange is completed by the high-temperature air. Three-stage compression centrifugal air compressor and its cooling water system and air system workflow as shown in Figure 1.
1.2 Working Principle of Screw Air Compressor: Suction Parameters
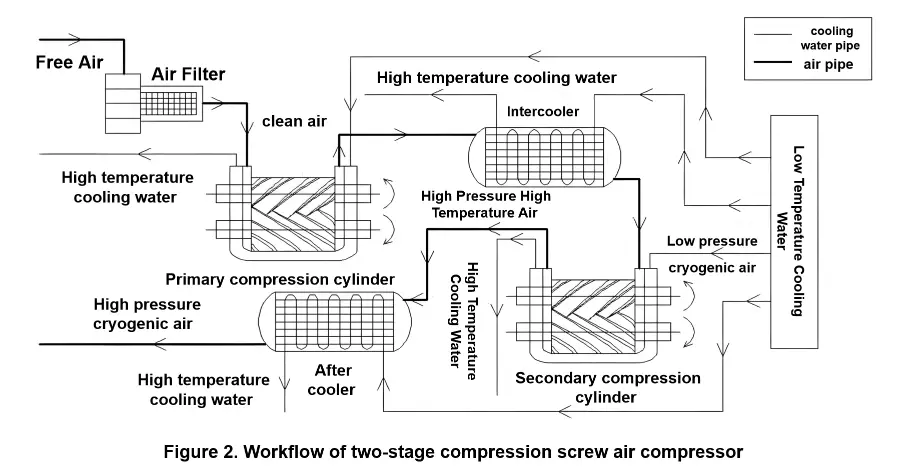
Screw air compressor relies on two parallel arrangement in the cylinder and engage each other ∞ shaped spiral rotor, according to a certain transmission ratio reverse rotation to complete the suction, compression and exhaust process, to produce compressed air. Inhalation, filtered clean air through the suction port into the inter-tooth volume between the two rotors, the inter-tooth volume between the two rotors with the screw rotation continues to increase, when the volume reaches its maximum value, and suction port disconnect, complete the suction process.
The compression process is completed by the continuous decrease of the inter-rotor volume, when the inter-tooth volume is connected to the exhaust port, the compression process is completed. This is followed by the exhaust process, in which the rotating screw delivers compressed air to the exhaust pipe until the inter-tooth volume is diminished. At the same time, cooling water flows into the cooler of each stage and outside the cylinder, and exits the cooler after completing the heat exchange with the hot air and cylinder. The working process of cooling water system and air system of two-stage compression oil-free screw air compressor is shown in Fig. 2.
2. Air Compressor Performance Analysis Method
Different types of air compressors work on different principles, so the suction parameters have different effects on performance. Due to the different air compressor suction state and air intake, the power difference is obvious. In order to facilitate the analysis, the suction parameters and power of the air compressor were selected and tested, and on this basis, the full efficiency and variable compression efficiency of the air compressor were analyzed and calculated, and the influence of suction parameters on the performance of the air compressor was studied. The full efficiency and variable compression efficiency are important indexes for judging the performance of air compressors. Under a certain air production pressure, the judgement of the performance of the air compressor mainly depends on whether the full efficiency is reduced. The calculation of the full efficiency of the air compressor can be expressed by formula (1):

Where: Pair is for the output compressed air effective pneumatic power KW; Pele is for the air compressor consumption of electric power, KW. Output compressed air effective pneumatic power Pair is compressed air flow, the compressed air flow beam contains the effective energy manifested in the form of power, can be calculated by the formula (2):
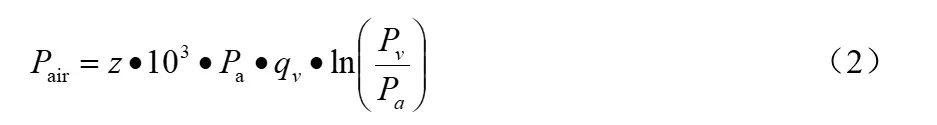
Where: z is the number of compression stages; Pa is the absolute pressure of the atmosphere MPa; qv is the volumetric flow rate Nm3/s in compression; Pv is the absolute pressure MPa in compression.
The actual work done by the air compressor is a multivariate compression process, and the multivariate efficiency is the ratio of the work consumed by the multivariate compression process to the work consumed by actual compression process. Multivariate compression efficiency ηs·n can be calculated by formula(3):
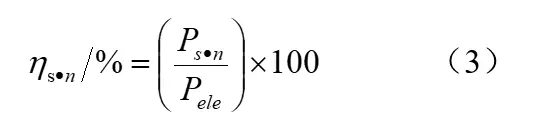
Where: Ps·n is the power of the multivariate compression shaft from the initial state to the final state KW. Multistage centrifugal air compressor whose multivariate shaft power can be calculated according to formula (4):
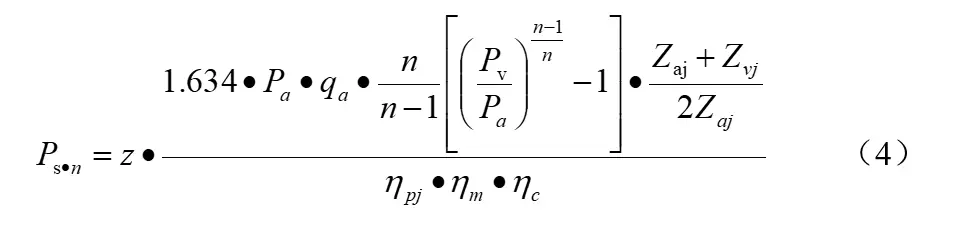
Where: q a is the volume flow rate at atmospheric pressure, m3/min; n is the multivariate index; Z a j, Z v j for the jth level of compression inlet and exhaust state of the compression coefficient, when the pressure is less than 2MPa, can be regarded as
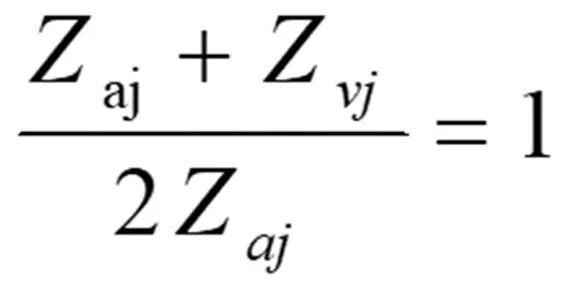
ηpjis the average multivariate index of compression process, take ηpj = 61.2%; ηm is the mechanical efficiency, when Ps·n = 1000~2000kW, ηm = 96%~97%, take ηm= 97%;ηc is the transmission efficiency, direct connection ηc = 1. Multi-stage screw compressor and its multivariate axial power can be calculated in accordance with equation (5):
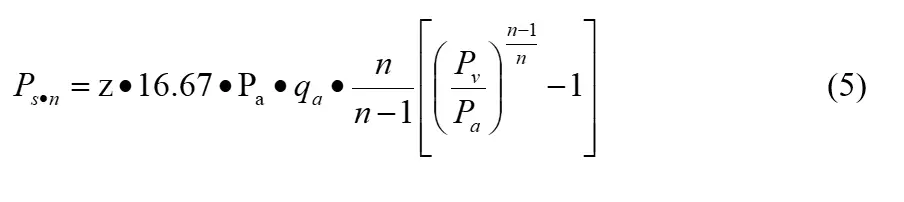
3. Analysis of the Effect of Suction Parameters on the Performance of Different Types of Air Compressors
3.1 Effect of Suction Temperature on Compressor Performance
The performance of an air compressor is inextricably linked to its suction temperature. The power and efficiency of screw and centrifugal air compressors suctioned at different temperatures were tested and analyzed when the humidity content of the air sucked in by the air compressor was 11.1g/kg (dry air) and 15.7g/kg (dry air), respectively, and the results of the tests are shown in Table 1.
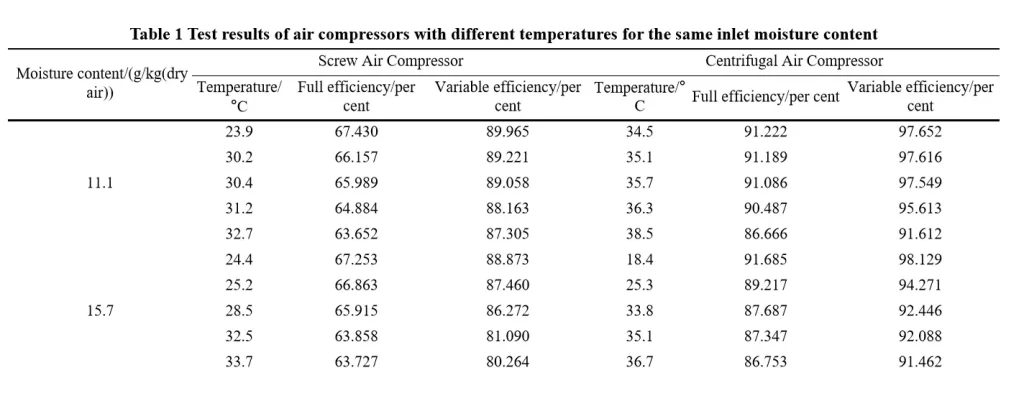
Through the test and analysis of the performance of air compressors with the same suction moisture content and different temperatures, it is found that the total efficiency and multivariate efficiency of centrifugal air compressors are significantly higher than that of variable frequency screw air compressors, and the effect of the suction temperature of air compressors on the performance of screw air compressors is more obvious than that of centrifugal air compressors.
In the case of the same moisture content of the suction air, the higher the suction temperature of the air compressor, the lower the operating efficiency, and when the temperature increases by 1°C, the total and multivariate efficiencies of the frequency-variable screw air compressor decrease by about 0.678% and 0.898%, respectively, while the total and multivariate efficiencies of the centrifugal air compressor decrease by about 0.517% and 0.832%, respectively. As the suction temperature increases, the multivariate efficiency of similar compressors changes more significantly than the total efficiency.
3.2 The Effect of Suction Air Moisture Content on the Performance of Air Compressor
The moisture content of the suction air has a great influence on the performance of the air compressor, in this experiment, we tested the screw air compressor suction air temperature of 25 ℃ and 31 ℃, as well as centrifugal air compressor suction temperature of 21 ℃ and 33 ℃, respectively, to analyse the power and efficiency of the air compressor that inhales air with different moisture content. Please refer to Table 2 for specific test results.
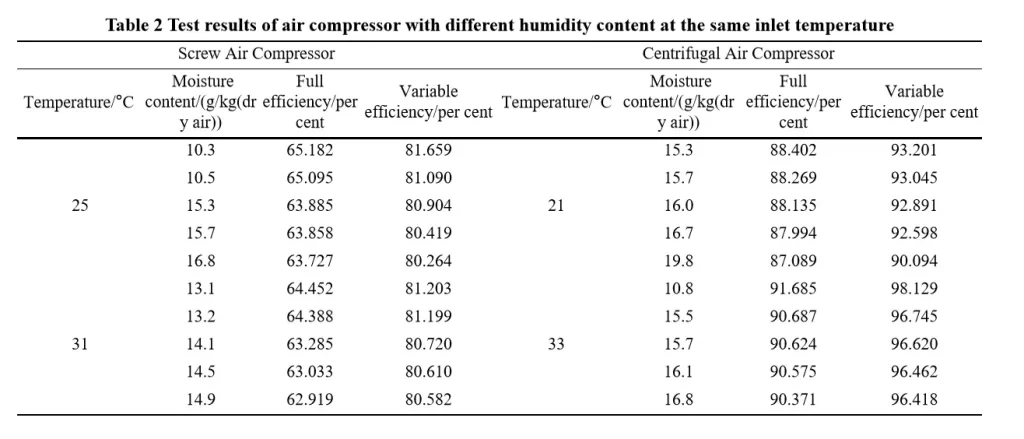
Through the testing and analysis of the performance of air compressors with the same suction temperature and different humidity content, it is found that: when the humidity content of the air compressor suction rises, the change in performance is slightly smaller than the increase in temperature. When the moisture content of the air compressor increases, the performance change of screw air compressor is more obvious than that of centrifugal air compressor.
When the suction temperature is the same, the higher the moisture content of the air compressor intake, the lower the operating efficiency. For every 1g/kg increase in moisture content (dry air), the full efficiency and multi-variable efficiency of the inverter screw compressor are reduced by about 0.457% and 0.644%, respectively; while the full efficiency and multi-variable efficiency of the centrifugal compressor are reduced by about 0.277% and 0.438%, respectively. In addition, when the suction temperature increases, the multivariate efficiency of similar compressors changes more significantly than the full efficiency.
3.3 Influence of Suction Enphalpy on Compressor Performance
Enthalpy is a compound state parameter of the work mass, and the enthalpy of wet air is calculated based on 1kg of dry air, i.e. the sum of 1kg of dry air enthalpy and dkg of water vapour enthalpy, and the enthalpy of wet air increases with the increase of temperature and humidity. This experiment aims to test and analyse the effect of different enthalpy values of intake air on the power and efficiency of the air compressor, and the test results are shown in Table 3.
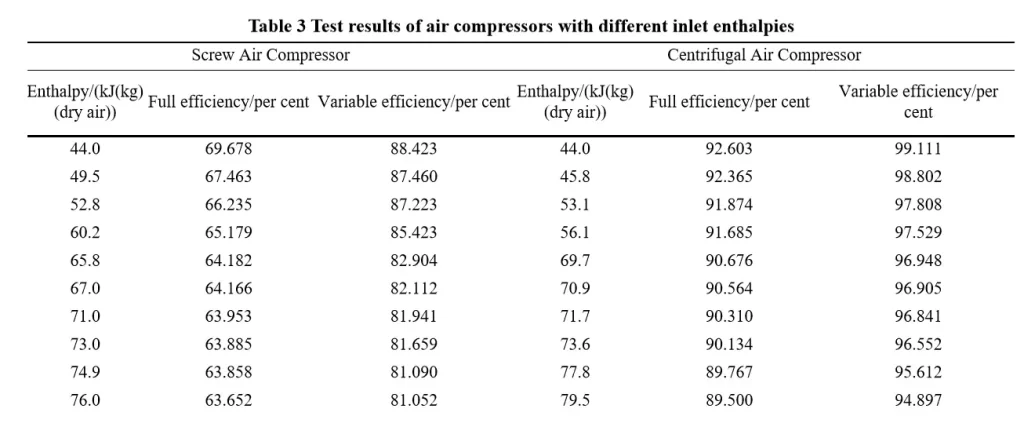
Through performance tests and analyses of air compressors inhaling air with different specific enthalpy, it was found that the efficiency of air compressors decreased when their inhalation enthalpy increased. When the enthalpy of air compressor intake increases by 1kJ/(kg (dry air), the full efficiency and variable efficiency of variable frequency screw air compressor decrease by about 0.155% and 0.235%, respectively; the full efficiency and variable efficiency of centrifugal air compressor decrease by about 0.125% and 0.151%, respectively. When the suction value increases, the change of variable efficiency of the same type of compressor is more obvious than the change of full efficiency.
4. Conclusion
In this paper, the efficiency of different types of air compressors under different suction parameters of air compressors in a textile enterprise is studied through a combination of experimental tests and theoretical calculations, and the following conclusions can be drawn from them:
- (a) The air compressors commonly used in textile factories are generally of two types: centrifugal and screw air compressors, in which centrifugal air compressors run more efficiently than screw air compressors, and if the enterprise has both centrifugal and screw air compressors, it should try to use centrifugal air compressors to produce compressed air in order to reduce the cost of compressed air production.
- (b) air compressor suction parameters are closely related to its performance, the temperature increases by 1 ℃, frequency screw compressor full efficiency and multi-variable efficiency were reduced by about 0.678%, 0.898%, centrifugal compressors were reduced by about 0.517%, 0.832%.
- (c) The moisture content of the inlet air is closely related to the performance of the compressor, when the suction temperature is the same, the moisture content increases by 1g/kg (dry air), the efficiency of the screw compressor decreases by about 0.457%, 0.644%, and the efficiency of the centrifugal compressor decreases by about 0.277%, 0.438%, respectively.
- (d) the enthalpy of the inlet air on the performance of the air compressor should not be ignored, when the enthalpy of the air compressor inlet air increased by 1kJ/kg (dry air), the screw machine efficiency decreased by about 0.155%, 0.235%, centrifugal efficiency decreased by about 0.125%, 0.151%.
- (e) When the inlet air parameters change, the screw machine than centrifugal efficiency changes are more obvious, and for the same type of compressor, when the suction parameter changes, its multi-variable efficiency is more significant than the full efficiency changes.
The energy consumption of the air compressor affects the energy consumption of the whole system and even the whole enterprise, the enterprise should actively take measures to reduce the temperature and humidity of the air inlet of the air compressor, improve the operating efficiency of the air compressor, reduce the energy consumption of the air compressor, reduce the production cost of the enterprise, and improve the competitiveness of the enterprise market. Read our new blog here.








